Gas Nitrocarburizing And Post Oxidation Processes For Shift Shaft 40CrH Steel
Gas gas nitrocarburizing process is a new chemical heat treatment process developed from liquid gas nitrocarburizing. The essence of gas nitrocarburizing process is low temperature nitriding. Gas nitrocarburizing process can improve the hardness, fatigue strength, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of parts.Due to the development of modern industry, more stringent requirements have been put forward for the surface properties of parts. In order to further improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the workpiece after nitriding, the nitriding + oxidation composite process has been produced.
A dense thin oxide layer (Fe0) formed after nitriding has low friction coefficient and high chemical stability, which improves the electrochemical performance of the surface of the nitriding, and significantly improves the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the nitriding layer.The nitriding layer is thin and brittle and easy to fall off, and the formation of oxide film is conducive to eliminating this shortcoming.In the 1980s foreign countries began to nitriding (nitrogen carbonization) oxidation complex process research.
The composite process of gas nitrocarburizing and post oxidation is a new metal surface strengthening modification technology, which can greatly improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of metal surface at the same time, and hardly deform the workpiece. Compared with the plasma nitrocarburizing oxidation composite treatment, the gas nitriding oxidation composite treatment has low requirements on the oxidation medium and treatment process. Meanwhile, in terms of the quality and performance of the infiltration layer, it has approached or even achieved the effect of salt bath gas nitrocarburizing and plasma nitrocarburizing oxidation in some parts processing process.Compared with QPQ process, gas nitriding oxidation combined treatment does not use cyanide to make up for the weakness of salt bath gas nitrocarburizing process containing toxic substances, so there is a certain improvement in the problem of public hazards. In addition, compared with the gas nitriding process, the gas nitrocarburizing process has the characteristics of short nitriding cycle, low treatment temperature and high performance of the permeability layer, and the surface hardness of the parts treated by the gas nitrocarburizing will not decrease even if the parts are reheated to the vicinity of the gas nitrocarburizing temperature.
Hangzhou Ruiqin Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd. studied the composite treatment of gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation on a 40CrH steel sample produced by a heat treatment plant, and compared it with the sample without oxidation treatment in the same nitriding process. After oxidation treatment, the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the material surface change.
- Test materials and methods
1.1 Equipment and materials
The combined treatment of gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation is carried out in the pit-type pre-vacuum nitriding furnace RGN. The size of the pre-vacuum nitriding furnace is 1500mm X 2000mm (diameter x height). The parts provided by the company are the shift shaft assembly material and the 40CrH steel parts that have been normalized. The specific dimensions are shown in Figure 1. After the parts are treated with gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation, in order to get better corrosion resistance, they are immersed in 30℃ oil for 15-20min and then dropped into the air to dry for 15-20mins.
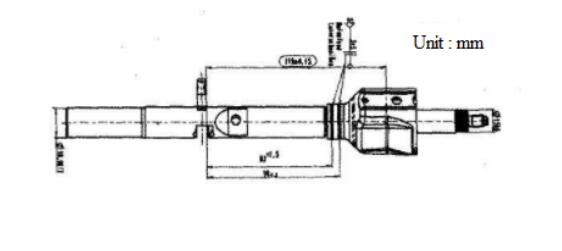
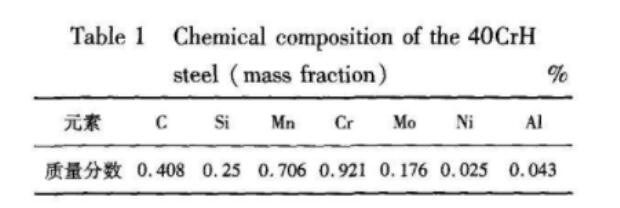
The sample used for the test is cut from the part by a wire electric discharge machine with a size of 18mm x 5mm. The surface of the sample was ground by a grinder to clean the surface with alkaline water and clean water, dehydrated and dried with anhydrous alcohol, and placed in a desiccator for later use. The chemical composition of the test steel is shown in Table 1.
1.2 Experimental program
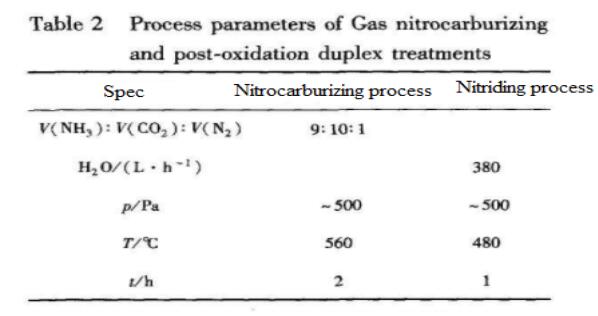
The combined treatment of gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation is divided into two stages: gas nitrocarburizing (gas carbon and ammonia co-infiltration) and gas oxidation treatment. According to the literature [11], in order to obtain better physical and chemical properties, the first stage soft nitriding treatment must obtain a white bright layer of e compound with a thickness of more than 10um. After the gas nitrocarburizing treatment, the carbonitriding gas is converted into an oxidizing gas, and the gas oxidation treatment is performed. According to the actual production status of a factory, the process parameters of the composite treatment are formulated, as shown in Table 2.
For the sample after the composite treatment, an 18KWD/MAX2500V+/PC X-ray diffractometer was used to analyze the phase of the infiltrated layer; the ZeissSigma-04-82 scanning electron microscope was used to observe the surface morphology of the sample and measure the thickness of the infiltrated layer; Measure the hardness distribution of the cross-section of the permeated layer with the MH-3 type microhardness tester; test the corrosion resistance of the composite layer through the anodic polarization curve experiment, and use the CHI600C electrochemical analyzer to measure the anode electrode of the gas (NC+0) permeated layer Chemical performance, the measurement is carried out in a room temperature 5% NaCl solution at a scanning rate of 5mV/s and a scanning frequency of 2Hz. The auxiliary electrode is a 260 platinum black electrode, and the reference electrode is a C(KS0)-1 mercury sulfate electrode.
2 Test results and analysis
2.1 The structure and structure of the gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer
The XRD diffraction results of the gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer show that the gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer is mainly composed of e and Fe0. Among them, e is the gas nitrocarburizing product Fe0, and the oxidation product a-Fe is the matrix.
Figure 3 shows the cross-sectional morphology of 40CrH steel after gas soft ammoniated and post-oxidized composite treatment. It can be found from the figure that the surface of the sample after the composite treatment is divided into two layers, namely the oxide layer and the nitriding layer. The outer surface layer is an oxide layer with a thickness of about 1~2um; the subsurface layer is a compound layer with a thickness of about 20pum; followed by a diffusion layer, and the matrix is a typical ferrite + pearlite mixed structure. It can be seen that the compound permeation layer is relatively dense and has a better bond with the matrix.
2.2 Hardness analysis of gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer
It is the microhardness distribution diagram of the cross-section of the gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer and the gas nitrocarburizing layer. From the results of the hardness gradient, it can be seen that the hardness value of the sample subsurface (about 10um deep from the surface) is the largest, which is due to the loose pores on the surface of the oxide layer. Comparing the results of the composite treated sample and the gas nitrocarburizing, the overall hardness value is not significantly reduced, and the hardness gradient change is maintained. After the composite treatment, the hardness is slightly reduced due to surface oxidation and decarburization, but because the friction coefficient of the FeO film is relatively low, the Fe0 film not only plays a key role in the corrosion resistance of the composite layer, but also reduces the oxidation after gas nitrocarburization. The friction coefficient of the composite layer and the anti-seizure ability of the surface of the material are improved. In addition, the surface hardness of the gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer is still 750HV. Compared with the matrix hardness, it is about 400HV higher and still has good wear resistance. Therefore, compared with the gas nitrocarburizing process, the gas nitriding and post-oxidation composite layer still maintains a good hardness and hardness gradient, and has better wear resistance.
2.3 Anodic polarization test of gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer
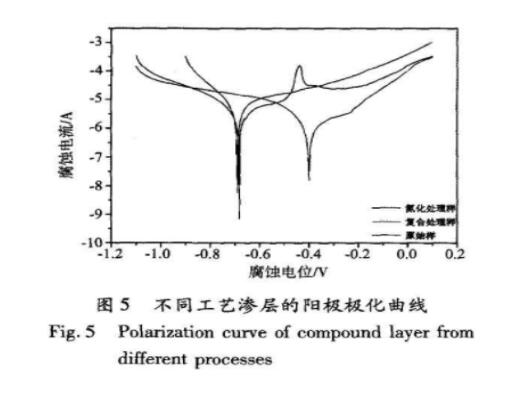
Figure 5 is the anodic polarization curve measured in a 5% NaC solution at room temperature after the nitriding treatment and the composite treatment. From the self-corrosion potential E and the self-corrosion current density 1-, the corrosion resistance of the material can be directly judged. Since! Is the most direct manifestation of the corrosion rate, the increase in corrosion resistance is based on 1 as the reference standard.
Conclusion
(1) The gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation composite layer is composed of a black dense Fe0 film with a thickness of 1um, an e white compound layer with a thickness of 20um, and a diffusion layer with a thickness of more than 100um.
(2) The gas nitriding and post-oxidation composite layer of 40CrH steel maintains a good hardness and hardness gradient compared with the surface hardened layer of gas nitrocarburizing.
(3) After 40CrH steel is treated with gas nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation, its corrosion resistance has been greatly improved.

QPQ Salt Bath Liquid Nitriding Process Quality Defect Analysis Controlled Atmosphere Pit Type Carburizing Production Line Equipment Planet Carrier Quenching And Tempering Furnace


Contact us
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *